Acme Packet’s session routing proxy (SRP), the Net-Net Session Router (SR), overcomes the challenges inherent in routing large numbers of SIP-based voice, video, instant messaging and multimedia sessions within and between the mobile, fixed-line and transit networks of service providers. The Net-Net SR plays a central role in Acme Packet’s Open Session Routing (OSR) architecture and leverages both internal and external best-of-breed routing databases using industry-standard protocols. The Net-Net SR configuration is supported on our hardware platforms—the Net-Net 4000 and 9000 series systems, and the Net-Net 4000 ATCA blade. It leverages our Net-Net OS software platform to offer industry-leading routing proxy capabilities in terms of SIP routing performance, routing control and deployment options, openness and interoperability, high availability and cost-effectiveness.
High-performance SIP routing – Acme Packet’s Net-Net SR is supported on three hardware platforms—the Net-Net 4000 and 9000 series and the Net-Net 4000 ATCA blade. On Acme Packet’s purpose-built hardware, transaction-stateful routing performance scales to 5400 SIP message per second, while stateless performance scales to 7500 messages per second. The ability of these platforms to maintain these performance levels reduces the number of session routing proxies required in a network, minimizing capital equipment and operating expenses.
Extensive routing control, flexible deployment options - Leading routing database products and services from Acme Packet ecosystem members are accessed via open, standards-based protocol interfaces such as ENUM, SIP, DNS, XML. These databases enable routing decisions for both the PSTN SS7/C7 and IP networks and include LNP, CNAM, LERG, E911, LCR, private and public ENUM and DNS. Routing decisions can be made using simple or very sophisticated combinations of parameters. Standard routing parameters include any combination of incoming network, destination number/URI, source number/URI, time/day, cost, carrier preference and codec. Acme Packet’s powerful SIP header and parameter manipulation rules enable routing by any number/URI in the SIP header.
Routing database information may be centralized or distributed to each Acme Packet SRP. When policy rules and route tables are provisioned locally, the SRP can scale to support up to 2 million routes. Larger numbers of dynamic or global routing rules are best supported using the high-capacity database products and services from Acme Packet’s OSR ecosystem members. These choices provide tremendous deployment flexibility and facilitate network evolution from small to large numbers of border points and from PSTN to IP network-focused connectivity.
Open, flexible and interoperable solution – From the perspective of SIP signaling within the 3GPP IMS architecture, the Acme Packet SRP serves as the Breakout Gateway Control Function (BGCF). This function is responsible for selecting the optimum session border controller or softswitch/media gateway for sessions leaving a provider’s network, and the Serving Call Session Control Function (S-CSCF) for incoming sessions. For session security, the SRP offers hardware-accelerated, high-performance, high-capacity IPsec and TLS encryption of SIP signaling. Interworking of SIP transport and encryption protocols and response codes is also supported. SRP configurations are available on Acme Packet-designed systems as well as the Net-Net 4000 ATCA blade platform for wireless and wireline ATCA chassis integration.
Carrier-class high availability – The Acme Packet SRP can continuously check external routing database availability and utilize back-ups in the event of database server or network failure. Similarly, the SRP can check egress SBC and softswitch/media gateway availability and re-route if required. SIP transaction load balancing is also supported across multiple SIP signaling elements. The SRP can also protect itself against malicious or non-malicious SIP DoS/DDoS attacks and overloads including mass calling events such as contest or entertainment televoting. In the event of failure of the primary active SRP, SIP messaging transaction state is check-pointed between active and standby units to ensure uninterrupted service.
Cost-effective, compact solution - In comparison with session-stateful, softswitch-based approaches, the compact high-performance Acme Packet SRP reduces capital and operational expenditures as service providers transition to and evolve their next generation networks.
Open Session Routing (OSR) architecture
Acme Packet’s Open Session Routing (OSR) architecture features the use of Acme Packet session routing proxies (SRPs) working in conjunction with a world-class ecosystem of routing database products and services from Acme Packet partners.
These complementary product vendors and service providers offer centralized routing databases and database provisioning tools for dynamic route selection. Acme Packet’s Net-Net SR, as well as the Net-Net Session Director (SD), queries these centralized databases using industry-standard ENUM, SIP and DNS protocols. The Net-Net SR’s local route tables may also be provisioned by 3rd party tools or the Acme Packet Net-Net EMS using XML. Using these databases, dynamic routing decisions within the core IP network and to the PSTN and other IP networks can be made using a wide selection of parameters.
The powerful combination of Acme Packet’s SRP and its partner ecosystem results in extremely fast session routing performance and increased network capacity, as well as lower overall network costs when compared to a solution in which the routing function is distributed among several SIP elements.
OSR addresses scaling problems when SIP session routing decisions become overly complex, requiring a dynamic, real-time routing decision for each individual session for multiple sources and destinations within a network. These source/destinations are other SIP signaling elements such as:
Wireless access network borders
Mobile Switching Centers (MSCs) connecting TDM-based 2G/3G radio access networks
MSCs or SBC/Multiservice Security Gateways (MSGs) connecting the Internet to femtocell and WiFi access points for UMA or I-WLAN services
SBCs connecting IP-based 3G/4G radio access networks
Wireline access network borders
CLASS 5 softswitches and SBCs connecting residential and business subscribers over DSL, cable and leased lines
SBCs connecting large enterprises and contact centers over SIP trunks
IMS service core access
IMS core elements connecting to access networks and interconnect networks
Interconnects/peering borders for wireless and wireline networks
SBCs connecting external service provider managed IP networks or the Internet
CLASS 4 softswitches and media gateways connecting to the PSTN
Figure 1 - Acme Packet Open Session Routing architecture

SRP functions and features


















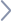














































































 京公網安備 11010502049343號
京公網安備 11010502049343號